Answer Relevancy: The Make-or-Break Metric for RAG Success
Answer Relevance
The common workflow of RAG applications starts with the user querying the system for information needs. The Retrieval component retrieves documents that are relevant to the user’s query from a knowledge base indexed in a vector store. The retrieved documents are used to generate a more concise and direct answer, effectively addressing the core inquiry. In other words, the Answer Relevance score measures the degree to which the user’s information need has been met.
In this post, let us walk through.
- The importance of the Answer Relevance score and why it is important than other RAG metrics
- Different approaches for estimating the Answer Relevancy score, and their pros and cons.
- Practical tips for implementation with examples.

Importance of Answer Relevance
Answer Relevancy is particularly crucial in RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) evaluation because it directly measures how well the system addresses what users actually asked for, which is often the primary failure point in RAG applications.
Here’s why Answer Relevancy stands out as especially important:
The Core Challenge of RAG Systems - RAG applications can technically retrieve relevant documents and generate fluent text, yet still completely miss the user’s intent. Answer Relevancy specifically measures whether the final output actually answers the question posed, making it a critical end-to-end metric.
User Experience Impact - In production RAG applications, irrelevant answers are often worse than admitting uncertainty. Users lose trust quickly when a system confidently provides detailed responses that don’t actually help them. Answer Relevancy directly measures this user-facing quality.
Holistic System Performance - While retrieval metrics tell you about one component and generation metrics about another, Answer Relevancy evaluates whether the entire RAG pipeline accomplished its fundamental purpose: providing relevant responses to user queries.
Estimating Answer Relevance Score
The two commonly used approaches to estimate the Answer Relevance score are -
- Generating Synthetic Questions. - A Reverse Engineering Approach
- LLM Evaluator
Generating Synthetic Questions - A Reverse Engineering Approach
With this approach, the questions are synthesized using the generated response as context. The Semantic Similarity score between the user query and the synthesized questions serves as a measure of the Answer Relevancy score. The intuition behind this approach is that, if the context can generate questions that are semantically similar to the user query, then the context should be relevant to the user query in the first place.
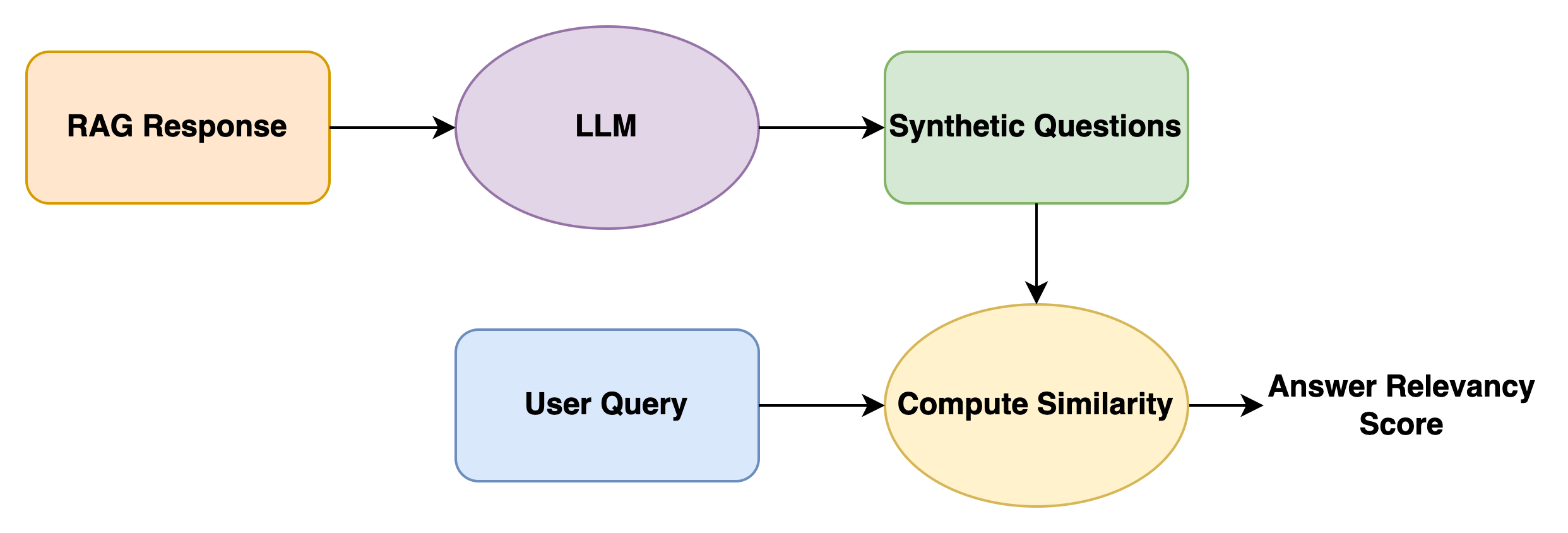
Formally,
\[Answer Relevancy Score = 1/N\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^N sim(q, q(i))\]Where
- q is the user query
- qg is the set of generated questions
This approach is adopted in the RAGAS framework.
Practical Tips
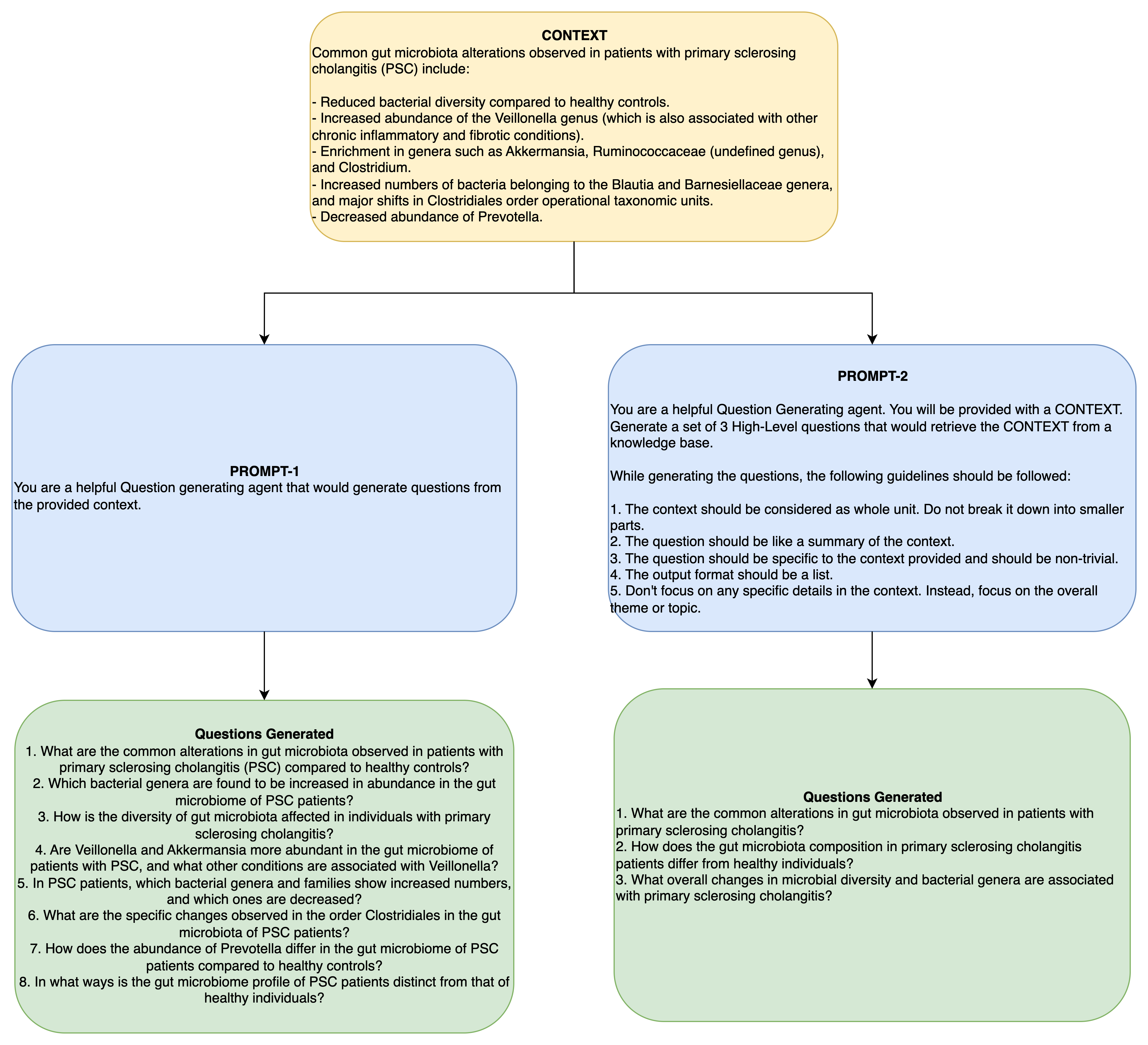
The prompt for synthesizing questions should impose strict guidelines on the type of questions to be generated, otherwise the generated questions will be highly specific focusing on any tangential or low-level details within context. The generated questions will be semantically divergent from the user query, resulting in low Answer Relevancy score.
Instead, the questions should be a very high-level focusing on the whole aspect or theme of the context provided. Also, it is recommended to restrict the number of questions generated from 3 to 5. Since, we are averaging the similarity scores, even one semantically divergent question can decrease the overall score. This will not give a true estimate of answer relevancy.
The following examples illustrates these concepts with examples from CUREv1 dataset.
LLM Evaluator
While the previous approach uses LLM to generate questions to estimate Answer Relevancy, there is another dominant approach - LLM as an Evaluator. This approach is being increasingly used in RAG applications. This approach outputs a relevance score either as a binary or discrete. It is not continuous as in the case of the former approach. Here are some examples for estimating Answer Relevancy using LLM.
Example - 1: Binary scores
Prompt used by the Langchain framework to compute Answer Relevancy score in binary.
"""You are a teacher grading a quiz. You will be given a QUESTION and a STUDENT ANSWER. Here is the grade criteria to follow:
(1) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER is concise and relevant to the QUESTION
(2) Ensure the STUDENT ANSWER helps to answer the QUESTION
Relevance:
A relevance value of True means that the student's answer meets all of the criteria.
A relevance value of False means that the student's answer does not meet all of the criteria.
Explain your reasoning in a step-by-step manner to ensure your reasoning and conclusion are correct. Avoid simply stating the correct answer at the outset."""
Example - 2: Discrete scores
Prompt to compute relevancy on a scale of 1-5.
"""You are an AI assistant responsible for evaluating the relevance of a RAG system's answer to a user's question [3, 1].
**User Query:**
{query}
**Generated Response:**
{response}
**Evaluation:**
1. Does the response directly and accurately address the user's query?
2. Does the response stay on the subject matter of the user's query?
Based on the above, provide a relevance score (1-5, where 5 is highly relevant) and a brief explanation for your assessment.
"""
References
- Y. Gao et al., “Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey,” Mar. 27, 2024, arXiv: arXiv:2312.10997. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2312.10997.
- S. Es, J. James, L. Espinosa-Anke, and S. Schockaert, “Ragas: Automated Evaluation of Retrieval Augmented Generation,” Apr. 28, 2025, arXiv: arXiv:2309.15217. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2309.15217.
- N. A. Sheikh, D. B. Marcos, A.-L. Jousse, A. Oladipo, O. Rousseau, and J. Lin, “CURE: A Dataset for Clinical Understanding & Retrieval Evaluation,” in Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining V.2, Aug. 2025, pp. 5270–5277. doi: 10.1145/3711896.3737435.
- https://github.com/explodinggradients/ragas
- https://docs.langchain.com/langsmith/evaluate-rag-tutorial#heres-a-consolidated-script-with-all-the-above-code
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: